Giant mantas, these captivating creatures of the sea, along with large sharks and bull sharks, never fail to leave scuba divers in awe. With their graceful movements, giant manta ray size dominates the underwater world. These sea creatures impress scuba divers with their impressive size, especially the giant oceanic manta rays. Despite their intimidating appearance, giant mantas are harmless filter feeders that pose no threat to humans.
They peacefully coexist with other sea creatures such as bull sharks. However, it is important to protect these gentle giants and their habitats from the impacts of fisheries. These gentle giants, also known as reef manta and oceanic manta, can reach astonishing widths of up to 29 feet, making them one of the largest species of rays in the world. They are not to be confused with the great white shark.
The immense size of giant manta rays becomes even more apparent when we compare it to everyday objects. The giant oceanic manta ray, known for its impressive width, is a sight to behold. Whether in the wild or in an aquarium, these majestic creatures captivate audiences with their sheer size. Picture this: a fully grown manta ray, a type of fish, can be as wide as a school bus! These magnificent reef manta rays have gills to breathe underwater and cephalic fins for navigation.
It’s hard to fathom how giant manta rays, including the giant oceanic manta ray and reef manta ray, effortlessly glide through the water with such elegance. The coloration of giant manta rays adds another layer of intrigue – their dark upper surface contrasts sharply with their white bellies, creating a striking visual spectacle in the aquarium. The fins of the spotted eagle ray are also a notable feature.
So buckle up and get ready for an adventure into the depths of the ocean where these incredible fish, giant manta rays, and oceanic manta rays roam freely in their natural habitat and can be observed in an aquarium.
Table of Contents
Manta Ray Size
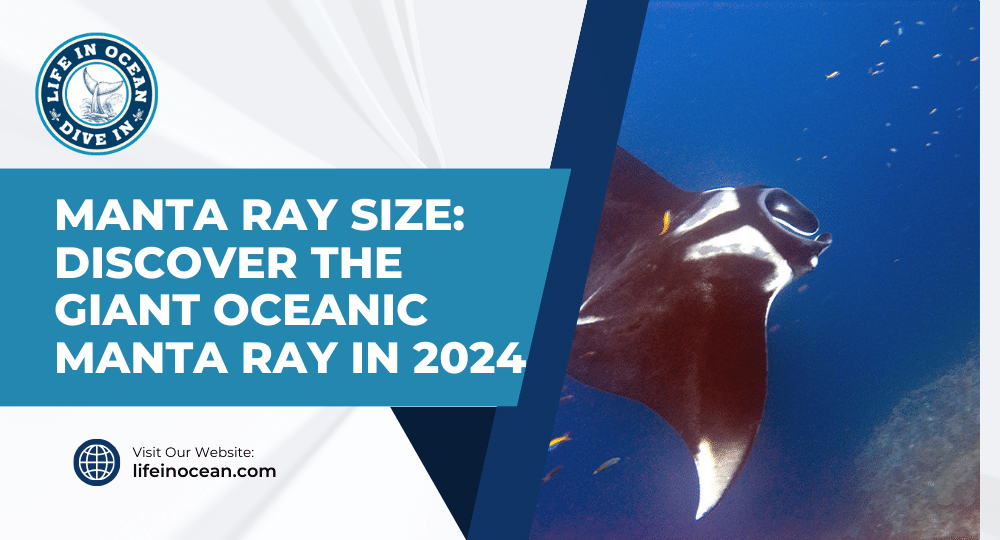
Manta rays, which are ft long fish, are truly remarkable creatures. One of the most fascinating aspects about them is their size. These giant manta rays, also known as oceanic mantas, can grow to be quite massive, with a wingspan that can reach up to an astonishing 25 ft, making them one of the largest species of ray in the ocean.
Impressive Wingspan
Their wingspan is truly awe-inspiring. Picture yourself standing next to a basketball hoop – that’s roughly how long the wings of giant manta rays, also known as oceanic manta rays, can stretch! These incredible creatures can have wingspans of up to 25 ft. With an average adult manta ray measuring around 15 feet from wingtip to wingtip, these gentle giants command attention wherever they go. The ft of a manta ray is truly impressive. The giant manta ray and oceanic manta ray, with their large wings, glide gracefully through the water, effortlessly navigating their surroundings.
Weighty Wonders
Not only do manta rays have impressive wingspans, but they also boast considerable weight. These incredible giant manta rays can weigh anywhere from 1,000 to 3,000 pounds depending on their size and age. The oceanic manta ray is truly a remarkable creature. That’s like having several small cars, including giant manta rays and oceanic manta rays, swimming right beside you! The weight of a manta ray is distributed across its broad body and flapping fins, allowing it to move smoothly through the water while maintaining its balance.
Growth and Development
Manta rays start off small when they’re born but quickly grow in size as they mature. Just like humans who experience growth spurts during adolescence, manta rays also undergo significant changes in size throughout their lives. As the oceanic manta ray and giant manta feed on plankton-rich waters and thrive in their marine habitats, these magnificent creatures gradually increase in both length and weight.
Comparing Sizes
To put the size of a manta ray into perspective, imagine two school buses parked side by side. That’s approximately how long some of these oceanic manta rays can be! However, it’s important to note that not all manta rays reach this colossal size; some individuals may be smaller or larger depending on various factors such as genetics, diet, and environmental conditions.
Awe-Inspiring Encounters
Encountering a manta ray in its natural habitat is an experience like no other. Imagine diving into the crystal-clear waters of the ocean and coming face to face with these magnificent creatures, the oceanic manta ray and giant manta. The giant manta ray’s sheer size and grace will leave you in awe, providing a humbling reminder of just how vast and diverse our oceans truly are.
Threats to Manta Rays

Overfishing
Overfishing poses a significant threat to manta rays. These gentle giants, known as ray, often get caught unintentionally in fishing nets, known as bycatch, while fishermen are targeting other species. This is a major concern because manta rays reproduce slowly and have a low population growth rate. The accidental capture of giant manta rays not only harms their population but also disrupts the delicate balance of marine ecosystems.
Habitat Destruction
The coastal development and pollution caused by human activities have led to habitat destruction for manta rays. As more coastal areas are developed for tourism or industrial purposes, the feeding grounds and breeding areas of these creatures, such as the ray, are being destroyed. The loss of these vital habitats disrupts the natural behavior patterns of rays and affects their ability to find food and reproduce.
Climate Change
Climate change is a big problem for manta rays and other sea animals. The ocean is getting hotter and the currents are changing. This makes it harder for manta rays to find enough plankton to eat. Plankton is an important food for them, and if there’s less of it, it affects the whole food chain. So, climate change is making it tough for manta rays to survive.
To combat these threats and protect manta ray populations worldwide, conservation efforts are crucial. Several organizations work tirelessly to raise awareness about the importance of preserving their habitats and implementing sustainable fishing practices.
Biology of Manta Rays
Manta rays are cool creatures that look like sharks but have their own special features. They have flat bodies and big fins that look like wings, so they can glide smoothly in the water. The ocean is home to some of the biggest manta rays, and it is truly awesome to see them grow really big. One thing that sets manta rays apart is their special mouth lobes. These lobes help them eat by filtering out tiny things like plankton from the water. Unlike other rays, mantas don’t have stinging spines on their tails. That means they’re safe to be around for people who want to swim or dive with them.
Manta rays are shaped in a way that lets them move easily in the water. They’re designed to be streamlined and save energy when they swim long distances. Manta rays have good senses that help them find food and get around in the ocean. Their eyesight is great, so they can see prey from far away. They also have special receptors that let them detect electrical signals from other animals. Manta rays can control their body temperature in certain parts of their body, which helps them stay warm when they’re active. Manta rays also form groups called aggregations for feeding or mating. Sometimes there can be lots of mantas in one group, which is really cool to watch.
Distribution and Habitat of Manta Rays
Manta rays are amazing animals that live in warm waters around the world. They like places with lots of plankton, which they eat. So, they travel to find the best spots with lots of food.
Coastal reefs and cleaning stations play a crucial role in serving as important habitats for manta rays during mating seasons. These locations provide not only protection but also opportunities for social interactions among these gentle giants. The presence of cleaning stations allows smaller fish known as cleaner wrasses to remove parasites and dead skin from the manta rays’ bodies.
Manta rays like to hang out in warm waters with lots of food. They do cool tricks as they swim around. They also like to eat plankton, which is like a buffet for them. Manta rays don’t like cold water, so they stay away from polar regions. It’s important to know where manta rays like to be so we can protect them.
Reproduction of Manta Rays
Female manta rays have babies every few years. It takes about a year for the babies to grow inside their mom’s body. When they are born, they are already 4 feet wide. Manta rays have special dances and swimming patterns when they want to find a mate. The dances help them communicate and decide if they are a good match.
There are two types of manta rays, reef mantas and oceanic mantas, but they both do the same mating rituals. After giving birth, female mantas feed their babies with special milk patches. Sometimes, pregnant mantas have to be careful of bull sharks near coral reefs. The coral reefs are important places for baby mantas to grow up because they have protection and food there. It’s important to study how mantas have babies so we can protect them for the future.
Fun Facts About Giant Manta Rays
Manta rays are truly fascinating creatures. Not only are they massive in size, but they also possess unique characteristics that set them apart from other fish species. Let’s dive into some fun facts about giant manta rays!
Largest Brain of All Fish Species
Did you know that manta rays have the largest brain of all fish species? This indicates their high level of intelligence and cognitive abilities. Just like humans, these magnificent creatures have complex brains that allow them to process information and make decisions. Their large brain size is a testament to their remarkable intelligence within the underwater world.
Speedy Swimmers
Despite their large size, giant manta rays are surprisingly fast swimmers. When necessary, they can reach speeds of up to 20 miles per hour! Imagine gliding through the ocean at such an impressive pace. These spotted eagle rays are graceful giants with the power and agility to swiftly move through the water, making them a sight to behold.
Acrobatic Maneuvers
Manta rays are big but graceful. They can do flips, twists, and turns underwater easily. It’s amazing to watch them glide through the water and show off their acrobatic skills. Giant manta rays are strong and elegant. They can navigate their marine environment with finesse. Now you know some cool facts about giant manta rays. They have a big brain and swim fast. They can also do acrobatics underwater. Scientists and marine enthusiasts are fascinated by the reef manta ray, these special creatures.
Conservation Issues Facing Manta Rays
International Trade in Manta Ray Products
The international trade in manta ray products, particularly their gill plates used in traditional medicine, is a major contributor to the declining populations of these magnificent creatures. The demand for these products has led to overfishing and exploitation of manta rays in many parts of the world. These gentle giants are often caught as bycatch or targeted specifically for their gill plates, which are believed to have medicinal properties.
Establishing Marine Protected Areas
Establishing marine protected areas (MPAs) is a crucial step towards conserving manta rays and their habitats. MPAs provide a safe haven where these vulnerable species can thrive without the threat of fishing and other harmful activities. By designating specific areas as protected zones, governments and conservation organizations can ensure that manta rays have the space they need to breed, feed, and migrate safely.
Implementing Fishing Regulations
In addition to creating MPAs, implementing fishing regulations is essential for the conservation of manta rays. This includes setting limits on catch sizes, prohibiting targeted fishing for mantas, and enforcing strict penalties for illegal fishing practices. By regulating fishing activities, authorities can help prevent further declines in manta ray populations and promote sustainable fishing practices that benefit both marine ecosystems and local communities.
Public Awareness Campaigns
Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in promoting the conservation of manta rays. By educating people about the importance of protecting these majestic creatures and their habitats, we can inspire individuals to take action. These campaigns can highlight the ecological significance of mantas as keystone species within marine ecosystems while also emphasizing the need for responsible tourism practices around them.
Ecotourism Initiatives
Ecotourism initiatives provide an opportunity to support both local economies and manta ray conservation efforts. Responsible ecotourism allows people to experience the beauty of these creatures up close while ensuring minimal disturbance to their natural behaviors and habitats. By participating in guided tours led by knowledgeable experts, visitors can learn about mantas and contribute directly to their conservation through fees that fund research, monitoring, and protection programs.
Conclusion
So there you have it, the fascinating world of manta rays and their incredible size. From their massive wingspan to their gentle nature, these magnificent creatures continue to captivate scientists and nature enthusiasts alike. We’ve explored the various factors that contribute to the size of manta rays, including their biology, distribution, and threats they face in the wild.
But it’s not just about their size; it’s about the importance of protecting these incredible animals and their habitats. By understanding the challenges they face and taking action to conserve their populations, we can ensure a future where manta rays continue to grace our oceans with their presence. So let’s do our part by supporting conservation efforts, advocating for sustainable fishing practices, and spreading awareness about these gentle giants.

Together, we can make a difference and secure a brighter future for these majestic creatures. Let’s protect them so that future generations can marvel at the awe-inspiring size and beauty of manta rays in the wild.
FAQs
How big can manta rays grow?
Manta rays can grow to impressive sizes, with the largest individuals reaching widths of up to 29 feet (8.8 meters) and weighing around 5,300 pounds (2,400 kilograms). That’s like having a small car gliding gracefully through the ocean!
What is the average size of a manta ray?
On average, adult manta rays have a wingspan of about 18 feet (5.5 meters) and weigh approximately 3,000 pounds (1,360 kilograms). They are still quite sizable creatures that command attention wherever they go.
Do all manta rays grow to the same size?
No, not all manta rays reach the same size. There is variation within the species, just like in any population. Some individuals may be smaller or larger than others due to factors such as genetics, diet, and environmental conditions.
How does the size of a manta ray compare to other marine animals?
In terms of sheer size, manta rays are truly remarkable creatures. While they may not be as massive as some whales or sharks, the biggest manta ray with their impressive wingspans make them one of the largest fish in the ocean. Imagine swimming alongside a giant underwater airplane!
Can you estimate a manta ray’s age based on its size?
Unfortunately, it is challenging to accurately determine a manta ray’s age solely based on its size. Unlike trees with growth rings or certain fish species with identifiable growth patterns, aging mantas remains difficult due to limited knowledge about their life cycle and growth rate.

