Imagine a world under the sea where different types of whales and dolphins live together in Shark Bay. These animals are really smart and have big brains. Scientists study their brains to understand how intelligent they are compared to humans. By comparing the cerebral capacity, brain sizes, and volumes of different species, we can gain insights into their thinking abilities. This research helps us understand the intelligence of different species. We will focus on comparing dolphin brains to human brains, specifically looking at the part called the cerebral cortex. Let’s dive into the fascinating world of dolphin intelligence and compare dolphins’ brains to the human brain.
Total Brain Size Differences Relative to Body Size
Dolphins and whales have bigger brains compared to their body size. Scientists think this helps them thrive in water. Chimpanzees also have big brains, but dolphins and whales have even bigger ones. This might be because of their unique adaptations to living in the ocean. Some people think chimpanzees’ big brains are connected to their social structures and behaviors.
Table of Contents
The Cetacean Cerebellum and Cerebrum
Highly Developed Cetacean Cerebellum
Whales and dolphins have a special part in their brains called the cerebellum. This helps them move and stay balanced. It’s even better developed than in chimpanzees. The cerebellum also controls the size of the brain and other parts inside the head. Just like whales, dolphins use their brains to do cool moves underwater. They can navigate and do tricks like chimpanzees. Whales are good at finding their way into the ocean because of their big brains. It’s like they have a built-in GPS.
Unique Characteristics of Dolphin Cerebrums
Dolphins have big brains that help them think and communicate. Even though their brains are not as big as humans or chimpanzees, they are still really smart. Dolphins use their brains to talk to each other and solve problems. Their brains are similar to the ones chimpanzees have.
Specialized Adaptations in Dolphin Brains
Dolphin brains have special adaptations that help them thrive in water. These adaptations are like what chimpanzees have. Dolphins have well-developed brain areas for echolocation, which is like seeing with sound waves. This ability is important for dolphins and other whales in the Balaenopteroidea family.
Studies have shown that cetaceans, such as whales and dolphins, have highly connected brains compared to other animals. The connectivity between different regions in their cerebrum is particularly remarkable. This enhanced connectivity facilitates efficient information processing and enables cetaceans, such as dolphins, to rapidly process sensory information due to their larger brain size and volume. Dolphin intelligence plays a crucial role in their ability to process information efficiently.
Surface Area of the Cerebral Cortex
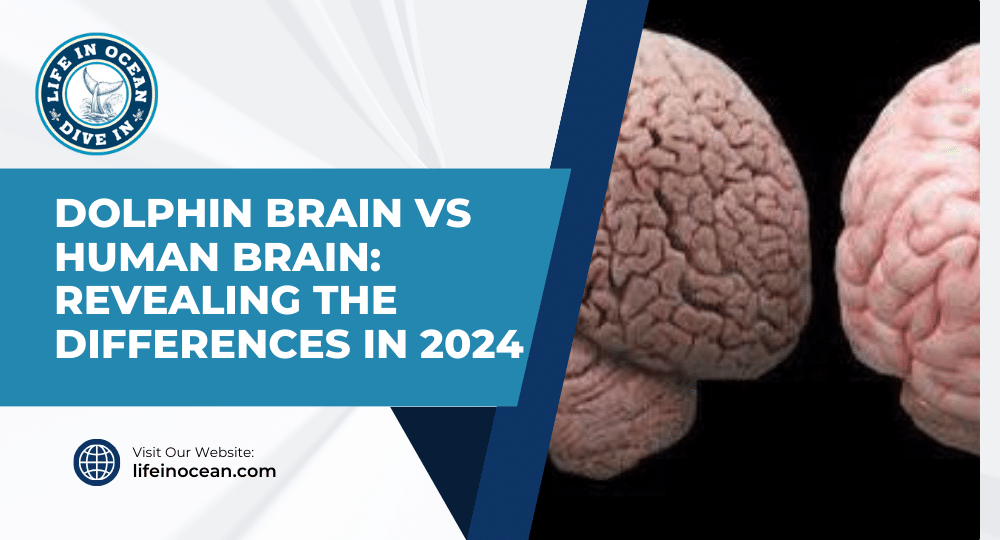
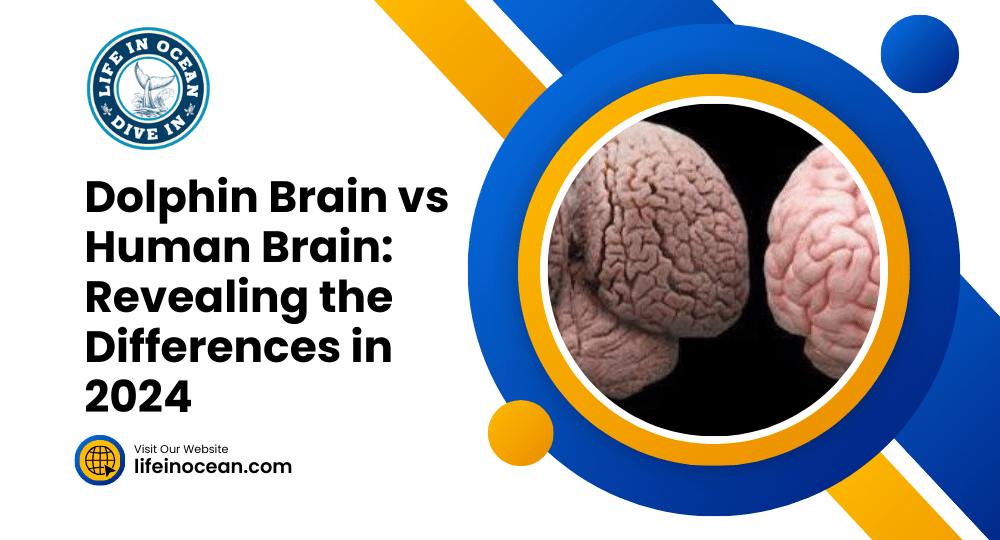
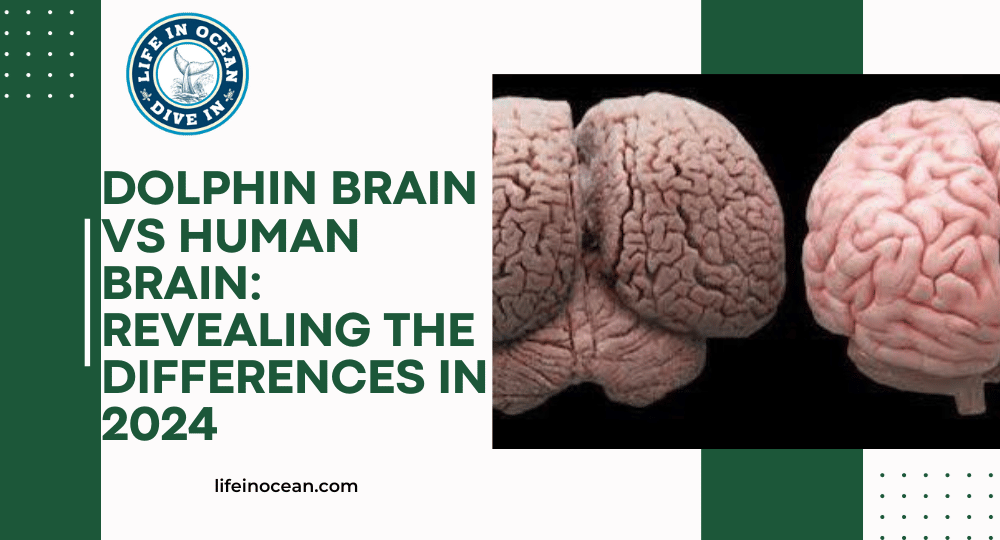
Dolphins have a bigger brain than humans. This means they might be better at understanding things. Dolphins have a part of their brain called the cerebral cortex, which helps them remember things and make decisions. They also have a part called the cerebellum that helps them move and stay balanced. Studies show that dolphins have bigger brains than humans. This could explain why dolphins are good at recognizing patterns, understanding social situations, and communicating. Their big brains make them different from other animals. So basically, dolphins are smarter than humans because of their big brains.
EQ and Endocranial Volume
To understand the differences between cetacean brains (such as whales and dolphins) and human brains, scientists use two important measures: EQ (encephalization quotient) and endocranial volume. These measures help compare the size of the cerebellum in both species. These measures help assess brain complexity and development across species, providing insights into intelligence levels of cetaceans. The size of the cerebellum is one of the points used to evaluate brain complexity and development.
EQ (Encephalization Quotient)
EQ measures the relationship between cerebellum volume and body mass. Researchers use regression analysis to find this relationship. The cerebellum volume helps determine brain complexity compared to body mass in animals like whales and dolphins. Both humans and cetaceans have high EQ values because of their big brains. Dolphins have large brains for their body size, just like humans. This is because dolphins have a well-developed cerebellum, which is common in balaenopteroidea species. Dolphin brain anatomy and size are fascinating dolphin brain facts.
Endocranial Volume Comparison
Scientists can study brain development by looking at the size of the cerebellum in cetaceans like dolphins and whales. The volume of the endocranium, which is the space inside the skull that holds the brain, is important for understanding the size and structure of their brains. By measuring body mass, researchers can learn about the overall size and capacity of different species’ brains, including cetaceans. Comparing cetaceans to humans, both have well-developed cerebellums. Dolphins and balaenopteroidea whales have similar endocranial volumes to humans, suggesting they have complex neural structures like us.s.
Assessing Intelligence Levels
By considering EQ, brain size, brain mass, and endocranial volume, scientists can conclude intelligence levels in dolphins versus humans and other cetaceans, such as whales. Despite having smaller overall brain sizes compared to humans, cetaceans such as dolphins exhibit high levels of cognitive abilities due to their large EQ values and significant endocranial volumes. This is especially true for balaenopteroidea whales.
Dolphins are known for their remarkable social behaviors, sophisticated communication skills, problem-solving abilities, and self-awareness—all indications of high intelligence.
Brain Structure
Dolphin Brains: A Unique Anatomy
Dolphin brains are interesting because they have a different structure than human brains. They have a special part called the cerebellum that helps with movement. Dolphins also have big brains compared to their bodies, just like humans. Their cerebrum, which is the smart thinking part of their brain, is different from ours. Dolphins have a unique cerebellum that helps them communicate and navigate in their groups. This means they might think differently or have special skills that humans don’t have. Dolphins also have a special part of their brain called the cerebellum that helps both sides of their brain communicate.
Human Brains: Anatomical Uniqueness
Dolphin brains are cool, but human brains have some special things too. Our brain has a big part called the cerebral cortex that helps us think better. It’s all folded up, which gives us more space for brain cells and makes us able to talk, solve problems, and be creative. We also have another part called the prefrontal cortex that helps us make decisions and be social. Dolphins have a good cerebellum that helps them move well. Both dolphins and humans need these brain things to do important stuff.
Brain Evolution
Dolphin Brain Evolution
Dolphin brain evolution has resulted in specialized adaptations for life in the aquatic realm. Cetaceans, such as dolphins, have developed unique features in their cerebellum to navigate and communicate effectively within their social groups. These adaptations allow them to thrive in their aquatic body and excel in their group dynamics. Cetaceans, including groups of dolphins and whales, have a large and highly developed brain, particularly in the cerebellum region, which enables them to thrive in their marine environment.
These intelligent creatures, with their dolphin brain anatomy and dolphin brain size, have adapted their bodies to excel in the ocean. When comparing the dolphin brain to the human brain, it’s fascinating to learn about dolphin brain facts. With their encephalization quotient comparable to that of humans, cetaceans such as dolphins possess remarkable cognitive abilities. These intelligent creatures have a large cerebellum, which contributes to their advanced brain functions. In addition, dolphins are known for their complex social behavior and ability to communicate in groups.
Human Brain Evolution
Our brain has evolved to help us survive and interact with others. One important part is the cerebellum, which helps us move and stay balanced. We also can form social groups and communicate in complex ways, which sets us apart from other animals like dolphins. These improvements in our brains have made our bodies and intelligence more advanced.
Our brains, including the cerebellum, have changed a lot over millions of years, leading to better thinking, problem-solving, and language skills. These changes have happened in different parts of our body and have made some traits go away. This evolution, influenced by brain size and changes, has shaped human civilization as we know it today. Different groups with different brain sizes have played a part in this process.
Comparing Brain Evolution
Dolphin and human brains evolved differently due to distinct challenges faced by these two groups of cetaceans and humans. Dolphins, a type of cetaceans, adapted to life in water by developing echolocation and good communication skills. Their adaptation is evident in their brain size and volume, as shown by the data. Humans evolved by using tools, developing language, and working together in groups. These adaptations have led to an increase in brain size and body complexity, distinguishing humans from other species such as cetaceans.
Both cerebellums and bodies changed in size over time due to different environments and needs of various groups. Scientists at Emory University studied brain sizes in humans, cetaceans, and other primates like chimpanzees and apes. They also examined the role of the cerebellum in these groups.
Problem-solving ability
Dolphins and humans are both smart and good at solving problems, but they do it in different ways because their brains are different. Dolphins use their intelligence to handle complicated situations, while humans use their brains to figure out hard problems. Both the dolphin brain and the human brain use their smarts to understand information and find answers. Studying how dolphins and humans solve problems helps us learn about their different ways of doing it. By looking at brain size and watching how they work together, we can learn more about how dolphins solve problems.
Dolphins have been seen working together to catch fish, which shows how smart they are. Humans have bigger brains compared to other animals, so they can think through complex problems and come up with logical solutions. Our brain size also helps us be creative and think of new ideas. Different groups have different brain sizes. Dolphins learn by trying different things until they find what works, while humans have different strategies for different problems.
Our cerebral capacity to think depends on our brain size and the information we gather. Depending on the situation, we might use logic or critical thinking to process information and make choices. Our brain size and group contribute to our ability to be creative and find new solutions. The data supports this idea.
Behavior
Dolphins are cool! They live in groups called pods and communicate with each other using sounds, movements, touch, and data. They’re smart with big brains and bodies. Humans are different because we have complex behaviors influenced by our culture and society. We have bodies, languages, customs, and traditions that shape how we act as a group. Studying dolphin behavior helps us learn about how dolphins’ brains and human brain animals live together in a group. By watching what they do and how they interact, we can learn important stuff about how they get along and how many of them there are. This tells us how dolphins move around and communicate.
Dolphins use their bodies and brains to explore and gather information. Humans use tools to build societies and survive. Learning about animal behavior also teaches us about their group size, body size, finding food, raising babies, and dealing with challenges in their environment. For example, scientists study how dolphins make friends and work together to find food. They look at the data to understand how their brains work when they collaborate. They team up and make plans to catch fish. Humans are different because our brains allow us to think and make choices based on new information or situations. Only our group can do this because we can use our bodies to think and figure things out.
Pod characteristics
Dolphins are social animals that live in groups called pods. They have complex behaviors and communicate with each other. Studying their behavior helps us understand how their brains work and how they interact with each other.
Dolphin Pods: Tight-Knit Social Groups
Dolphin pods are like friend groups that stick together and do things as a team. They use their brain and body to figure out what’s happening around them. Scientists study them to learn about how dolphins act in groups. Dolphins work together to find food, stay safe, and take care of their babies. They use data to plan their actions. It’s like they have their own squad goals!
Human Social Groups: Diverse Affiliations
Humans have different social groups like families, friends, coworkers, and classmates. These groups affect our body and brain. Families are important because they give us love and support. Friends are people we choose to hang out with based on shared interests. Coworkers are part of our work network as we try to achieve goals together. Classmates bond over shared school experiences. All these groups shape our lives and influence our bodies and brains.
Complex play
Dolphins and humans both engage in complex play behaviors that contribute to their brain development, group dynamics, body coordination, and the collection of data for learning, creativity, and emotional well-being. Dolphins are known for their elaborate play activities, which involve games, toys, and acrobatics, and stimulate the brain and body. These playful behaviors also generate valuable data for researchers studying dolphin behavior in groups. Similarly, human play encompasses a wide range of activities that stimulate the brain and promote social interaction within a group. Play engages the body and mind, fostering mass participation and creating opportunities for data collection and analysis.
Contrasting Complex Play Behaviors
Dolphins and humans both play in different ways, but it helps their brains and groups. Dolphins do physical games underwater to show how agile they are. Humans have activities on land that make their brains think and bring people together. Dolphins use toys or things they find in their environment to play, and humans use props or equipment to make their activities more fun. Both dolphins and humans benefit from playing because it helps their brains and brings them closer as a group. Playing is important for dolphins because it helps them survive and be social with their pod. Playing also helps the dolphin’s brain grow.
Cross-species cooperation
Dolphins are smart animals that work well together with other creatures. They can team up with humans and whales to achieve common goals. This shows how different species can cooperate. Dolphins use their brains to communicate and work together as a group. Humans also study dolphins to learn about their behavior and intelligence. Sometimes dolphins and humans even fish together to catch more fish. Young dolphins learn from older dolphins and other species, which helps them survive in the ocean. Dolphins also collaborate with whales and sharks, showing their social skills. All of these things make dolphins successful and intelligent. Dolphins and whales also cooperate.
Creative behavior
Dolphins and humans are both creative thanks to their brains. Dolphins show their creativity by using clever hunting techniques and playing with objects. Their big brains let them do these cool things. Humans also have creative brains and express them through art, music, inventions, and more. Our brains help us be creative and have done so throughout history to make lots of cool stuff.
Dolphins: Novel Behaviors in Hunting and Play
Dolphins are smart and can do cool things. They use their big brains to come up with new ways to hunt for food. Some dolphins even use sponges as tools to protect themselves while they search for food on the ocean floor. This shows that dolphins are good at solving problems and thinking of creative solutions.
Also, dolphins like to play with stuff they find in the water. They might play with pieces of wood or throw seaweed or fish in the air. This is because dolphins have big brains and like to have fun. Playing helps them learn about their environment and try out different ways of doing things. It’s like exercise for their brains.
Humans: The Multifaceted Nature of Creativity
Humans are naturally creative because of their brains. Our brain helps us think creatively and come up with new ideas. We can see this throughout history in things like cave paintings and modern inventions. Artistic activities like painting, music, and writing allow people to express themselves and inspire others. Inventions like the wheel and electricity have also made a big impact on society. Creativity goes beyond just art.
Communication
Dolphins and humans communicate differently. Dolphins use sounds, body language, echolocation, and their brain to talk to each other and find their way. Humans have many ways to communicate, like talking, writing, and using technology. Our brain helps us in all of these ways. Dolphins use special whistles to recognize each other. Humans have complex brains with lots of words and grammar rules. We can write things down and remember them later. Our brain is amazing at saving important ideas and memories. Dolphins are smart and can learn tricks and solve puzzles. Humans can learn too, in school or through personal experiences. Our brain helps us think and understand different subjects.
Self-awareness
Dolphins and humans both possess self-awareness, a crucial aspect of brain consciousness and personal identity. However, how this self-awareness is demonstrated differs between the two species’ brains.
Dolphins exhibit self-awareness as demonstrated by mirror self-recognition tests.
In studies conducted using mirror self-recognition tests, dolphins have shown signs of self-awareness in their brains. These brain tests involve placing a mark on an individual’s body that can only be seen through a mirror reflection. If the individual recognizes their brain in the mirror and attempts to investigate or remove the mark, it indicates an understanding of their physical appearance. Dolphins have displayed such behavior, indicating that they possess a level of self-perception in their brain.
Human self-awareness is a fundamental aspect of consciousness and personal identity.
For humans, self-awareness is deeply ingrained in our daily lives. It is a fundamental aspect of the human brain and is essential for our overall well-being. The brain allows us to recognize ourselves as individuals separate from others and understand our thoughts, emotions, and actions. It is the key organ responsible for these functions. This brain awareness contributes to our sense of identity and shapes how we interact with the world around us.
Contrasting self-awareness sheds light on the cognitive capacities related to self-perception in dolphins versus humans.
When comparing dolphin and human self-awareness, it becomes evident that there are unique brain cognitive capacities at play in each species. While dolphins demonstrate an ability to mirror self-recognition, it is important to note that their understanding of all may differ from ours due to differences in brain structure and function.
The dolphin brain possesses remarkable intelligence al, but it operates differently than the human brain. Dolphins have highly developed brains, social structures, and complex communication systems underwater. Their brains have evolved to excel at tasks related to navigation, echolocation, and social interactions within their marine environment.
Dolphin intelligence poses tricky scientific and ethical questions
Dolphins: The Clever Cogs of the Sea
The remarkable intelligence displayed by dolphins has fascinated scientists and sparked intriguing inquiries about animal cognition in the brain. These dolphin intelligent aquatic creatures, known for their playful nature and remarkable communication skills, have brains that are surprisingly similar to our own. Al Researchers have discovered that dolphin brains share several structural features with human brains, such as a large neocortex—the part responsible for higher-order thinking.
Ethical Considerations in Assessing Dolphin Intelligence
Assessing the intelligence of dolphins raises ethical questions due to their potential moral standing and the complexity of their brain. As we uncover more about the brain and cognitive abilities of these marine mammals, it becomes crucial to consider how this knowledge impacts our treatment of them. Some argue that if dolphins possess a high level of intelligence comparable to humans, they should be afforded certain rights and protections for their brains and al. This perspective challenges our traditional understanding of intelligence and prompts us to reevaluate our relationship with animals, particularly in terms of their brain capabilities.
Beyond Human Boundaries: Rethinking Intelligence
Dolphin intelligence pushes us to broaden our understanding of the brain and intelligence beyond human boundaries. While humans have long considered themselves the pinnacle of intellectual prowess, studying dolphins challenges this notion. Dolphins possess an incredibly complex brain, which raises questions about our understanding of intelligence. These intelligent creatures exhibit complex problem-solving skills, social behaviors, and self-awareness—traits once thought exclusive to humans. By examining the cognitive abilities of dolphins, we gain valuable insights into the diverse ways in which intelligence can manifest in different species, including the brain.
Unlocking the Secrets of Dolphin Behavior
Researchers continue to delve into the intricacies of dolphin behavior to understand the workings of their remarkable brains. One fascinating study conducted by Marino et al. focused on the brain of bottlenose dolphins residing in Shark Bay—a unique habitat off Western Australia’s coast.
Conclusion: Dolphin Brain vs Human Brain
So, there you have it! We’ve explored the fascinating world of dolphin brains and compared them to our own. Dolphins possess remarkable intelligence and cognitive abilities that rival those of humans in many ways. The dolphin brain is truly impressive. From their problem-solving skills to their use of tools and communication methods, dolphins continue to amaze scientists and challenge our understanding of animal intelligence. The brain of a dolphin is truly remarkable.
But why does this matter? Well, understanding the complexity of dolphin brains not only sheds light on the evolution of intelligence in different species but also raises important ethical questions. As we gain more knowledge about the brains of these incredible creatures, we must consider how our actions impact their brain, lives, and habitats. It’s up to us to protect these intelligent brain beings and ensure their survival for future generations.
So, the next time you catch a glimpse of a dolphin swimming gracefully in the ocean, remember the incredible brainpower that lies beneath the surface. Let’s continue to learn from these amazing creatures and their incredible brains, and work towards a future where we coexist with them in harmony.
FAQs
Is a dolphin’s brain bigger than a human’s brain?
Yes, a dolphin’s brain is larger than a human’s brain. While the average adult human brain weighs around 1.3 kilograms, a dolphin’s brain can weigh up to 1.7 kilograms.
Are dolphin brains more advanced than human brains?
Dolphin brains have evolved differently from human brains, allowing them to excel in certain areas such as echolocation and social communication. However, it is important to note that both dolphin and human brains are highly complex and specialized in their ways.
Can dolphins think like humans?
While dolphins possess high cognitive abilities and exhibit problem-solving skills, their brain thinking processes differ from those of humans. Dolphins have a unique brains, sensory perceptions, and social structures that shape their thinking patterns.
Do dolphins have emotions like humans?
Dolphins, like humans, display a wide range of emotions that are connected to the brain. The brain of dolphins enables them to experience joy, grief, anger, and empathy towards others within their pod or group.
Who has a better memory: dolphins or humans?
Dolphins have remarkable brains with long-term memory capabilities that surpass those of humans in certain aspects. Their ability to recognize individuals and remember complex vocalizations over extended periods is truly impressive.

