“Life is too short for people to sleep without style in their beds during the day, like the payjama shark.” – Unknown
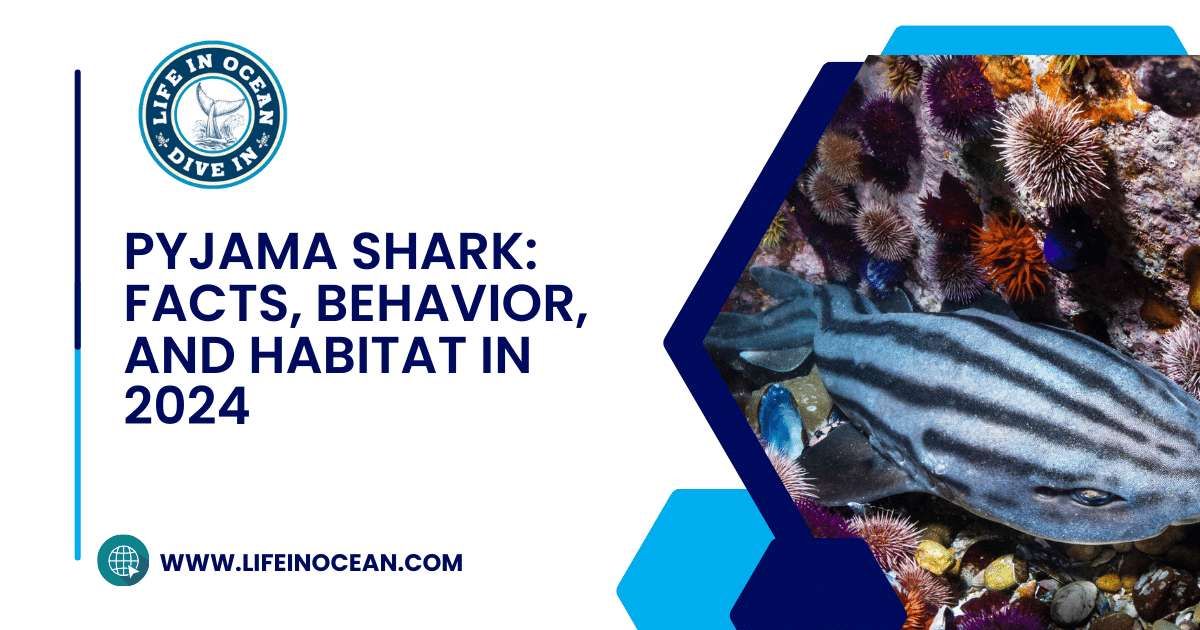
Get ready to dive into the fascinating world of striped catsharks! These sharks can be found in shallow waters and are often seen swimming alongside other fishes. They are also a common sight for fishermen. These small, bottom-dwelling creatures like the pajama shark and striped catshark are a common sight in the coastal waters of South Africa. They can be found on the ocean floor and are often encountered by local fishermen. With their distinctive striped pattern resembling pajamas, pyjama sharks, also known as catsharks, stand out among their larger counterparts.
These sharks can be found on the ocean floor at depths ranging from inches to feet. Found in shallow waters, these catsharks are known for their unique coloration and playful nature. They can grow up to 24 inches (61 cm) in length, making them a popular choice for aquarium enthusiasts. Join us as we explore the intriguing characteristics and behavior of these captivating striped catsharks, which can grow up to 24 inches (61 cm) in length. From their habitat preferences to their interactions with other fish species, we’ll uncover the secrets of these charming underwater residents, such as the pajama shark and the striped catshark, which can grow up to several inches in length.
Table of Contents
Understanding the Pyjama Shark Species
The pyjama shark, also known as the striped catshark or pajama catshark, belongs to the family Hemiscylliidae. Within this family, there are two recognized species: the striped catshark (Poroderma africanum) and the payjama shark (Poroderma pantherinum).
Pyjama sharks are fascinating creatures with distinct characteristics. The striped catshark earned its name due to its unique pattern of dark stripes resembling a set of pajamas. These striped catsharks, also known as pajama sharks, use their stripes for camouflage to blend in with their surroundings on the ocean floor.
The striped catshark, Poroderma africanum, is commonly found along the coastlines of South Africa and Mozambique, while the pajama shark, Poroderma pantherinum, is primarily found around Madagascar and nearby islands. Both species share similar physical traits and behaviors.
These striped catsharks have slender bodies that can reach up to 1 meter in length. The striped catshark, also known as the pajama shark, possesses broad heads with small eyes and nasal barbels that help them detect prey hidden within sandy or rocky crevices. The diet of the striped catshark, also known as the pajama shark, mainly consists of small fish, crustaceans, and mollusks.
One interesting characteristic of striped catsharks, also known as pyjama sharks, is their ability to breathe even when stationary on the seabed. They accomplish this by pumping water over their gills using a mechanism called buccal pumping. The pajama shark and striped catshark accomplish this by pumping water over their gills using a mechanism called buccal pumping.
Despite being relatively small in size compared to other shark species, pyjama sharks play an important role in maintaining the balance of marine ecosystems. As bottom-dwelling predators, pajama sharks help control populations of smaller organisms, contributing to overall ecosystem health.
Habitat and Geographical Distribution
Pyjama sharks, also known as striped catsharks, can be found in the shallow coastal waters along the southwestern coast of South Africa. These pajama sharks, known as cool cats, prefer to hang out in rocky reefs, kelp forests, and sandy bottoms, which provide them with both shelter and hunting grounds.
Their distribution ranges from False Bay to Port Elizabeth, encompassing a variety of habitats within this stretch of coastline where the pajama shark can be found. You can catch these sleek pajama sharks in intertidal zones, where they might take refuge in caves or explore the nooks and crannies of rocky outcrops. The pajama shark is equally at home in the open waters just off the coast or even on the ocean floor.
This species has adapted well to their inshore environment, thriving along the western cape of South Africa. They have developed unique characteristics that allow them to blend seamlessly into their surroundings and ambush unsuspecting prey.
The pyjama shark’s ability to inhabit such a diverse range of habitats makes it an important part of local ecosystems. It plays a crucial role in maintaining balance within fish populations by preying on smaller species.
Understanding the habitat and geographical distribution of pyjama sharks is essential for conservation efforts and sustainable fisheries management. By protecting these coastal areas and implementing responsible fishing practices, we can ensure that future generations will continue to encounter these fascinating creatures off the shores of South Africa.
Physical Characteristics and Identification
Pyjama sharks, scientifically known as Poroderma africanum, are small-sized species of sharks with slender bodies that can reach a maximum length of around 1 meter (3 feet). These sharks have a distinctive appearance, characterized by dark vertical stripes running along their body.
The dark stripes serve as camouflage for the pyjama shark in its natural habitat. They help the shark blend in with its surroundings, making it less visible to potential predators or prey.
Pyjama sharks possess two dorsal fins located towards the posterior end of their body. These fins aid in stability and maneuverability while swimming through the water.
In addition to their unique markings and dorsal fins, pyjama sharks also have other physical features worth noting. They have pectoral fins that help them navigate and steer through the ocean depths. Their bodies are typically dark brown in coloration.

Pyjama sharks have thin tricuspid teeth that enable them to capture and consume their preferred diet of bony fish and crustaceans.
Overall, pyjama sharks can be easily identified by their small size, distinct dark stripes, presence of dorsal fins towards the posterior end of their body, and slender physique.
Key Points:
- Pyjama sharks have slender bodies with a maximum length of around 1 meter (3 feet).
- They have distinct dark vertical stripes running along their body.
- These sharks possess two dorsal fins located towards the posterior end of their body.
- Pectoral fins aid in navigation.
- The species is scientifically known as Poroderma africanum.
- They primarily feed on bony fish and crustaceans.
- Pyjama sharks are small-sized species with unique physical characteristics.
Biology, Behavior, and Ecology
Nocturnal Predators
Pyjama sharks are known for their nocturnal habits, preferring to hunt and feed during the night. They have a unique adaptation that allows them to see in low-light conditions, making them efficient hunters in the darkness.
Varied Diet
These sharks have a diverse diet, feeding on various small benthic organisms. Their menu includes crustaceans like crabs and shrimp, mollusks such as clams and snails, and even small fish. This wide range of prey ensures that pyjama sharks can find sustenance in different habitats.
Utilizing Tidal Pools
One interesting behavior observed in pyjama sharks is their use of tidal pools during low tide as feeding grounds. These shallow pools provide an abundance of food sources for the sharks to feast upon. It’s like having a buffet right at their doorstep!
Habitat Preference
Pyjama sharks are commonly found along the coasts of South Africa, particularly around rocky reefs and kelp beds. These areas provide ample hiding spots for the sharks during the day when they rest.
Adaptations for Survival
To survive in their habitat, pyjama sharks possess several adaptations. Their slender bodies allow them to maneuver through tight spaces within rocky crevices, while their camouflaged coloration helps them blend into their surroundings. These adaptations aid in both hunting prey and avoiding potential predators.
From being skilled nocturnal predators to utilizing tidal pools as feeding grounds, pyjama sharks showcase fascinating biology, behavior, and ecology. Their ability to adapt to different environments contributes to their survival in coastal habitats.
Reproduction and Lifecycle
Female pyjama sharks have a unique way of reproducing. They are what we call oviparous species, which means they lay eggs that develop externally before hatching. These eggs are enclosed in protective cases called egg cases.
The female pyjama shark attaches these egg cases to rocks or other substrates for added protection. It’s like she’s saying, “Hey, I want my babies to be safe and sound!” The egg cases provide a cozy home for the developing embryos inside.
After a gestation period of several months, the young hatchlings finally emerge from their snug little homes fully formed and ready to explore the big blue ocean. It’s like they’re bursting out of their shells, eager to start their journey.
Imagine this: a tiny pyjama shark pup breaking free from its egg case and swimming off into the vast underwater world. It’s like watching a baby bird leave its nest for the first time – both exciting and a little nerve-wracking!
Interestingly, each egg case usually contains only one precious little shark embryo. It’s not like those invertebrates that can lay hundreds or even thousands of eggs at once! Pyjama sharks take things slow and give each offspring individual attention.
So, when you see a pair of adult pyjama sharks swimming together in the ocean, you might wonder if they’re planning on starting a family soon. And yes, chances are they might be looking for the perfect spot to lay an egg case with just one special little sharky inside.
That wraps up our discussion on the reproduction and lifecycle of pyjama sharks! Now you know how these fascinating creatures bring new life into the world.
Diet and Predatory Relationships
Pyjama sharks have a diverse diet, mainly feasting on benthic invertebrates. These underwater creatures make up the majority of their meals. With their sharp teeth, pyjama sharks can crush and consume prey items like crabs, shrimps, and small fish.
These sharks are not picky eaters. They’ll gobble up anything that comes their way as long as it fits into their mouth! Their strong jaws and teeth enable them to break through the hard shells of crustaceans and devour them with ease.
However, pyjama sharks aren’t always at the top of the food chain. Larger predators such as larger sharks and seals may consider these little guys as a tasty snack. It’s a tough world out there for our striped friends!
Pyjama sharks don’t pose much of a threat. They are not typically targeted by commercial fisheries or anglers for sport fishing purposes. However, they can sometimes end up as bycatch in fishing nets meant for other species.
In kelp forests, pyjama sharks find ample opportunities to hunt among the swaying seaweed. The kelp provides cover for both predators and prey, creating an ecosystem where these striped hunters can thrive.
To summarize:
- Pyjama sharks have a varied diet consisting mainly of benthic invertebrates.
- They use their sharp teeth to crush and consume prey items such as crabs, shrimps, and small fish.
- Larger predators like larger sharks and seals may prey on pyjama sharks.
- While they are not targeted by commercial fisheries or anglers, they can become unintentional bycatch.
- Kelp forests provide an ideal hunting ground for pajama sharks due to the abundant cover it offers.
Conservation Status and Human Impact
Pyjama sharks, also known as striped catsharks, are currently listed as “Least Concern” by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). This means that their overall population is considered stable and not at immediate risk of extinction. However, despite this designation, pajama sharks still face potential threats from human activities and habitat degradation.
One significant impact on pajama shark populations comes from coastal development. As humans continue to build along coastlines, it often leads to the destruction and alteration of critical habitats where these sharks reside. Coastal development can result in the loss of important breeding grounds and feeding areas for pyjama sharks.
To ensure the long-term survival of pyjama sharks, it is crucial to implement sustainable fishing practices. Overfishing can significantly impact their populations by depleting their numbers faster than they can reproduce. By adopting sustainable fishing methods such as catch limits, size restrictions, and using selective gear, we can help protect pyjama shark populations from being overexploited.

Another effective conservation measure is the establishment of marine protected areas (MPAs). These designated zones help safeguard critical habitats for various marine species, including pyjama sharks. MPAs provide a safe haven where these sharks can thrive without disturbance or excessive human interference.
By combining sustainable fishing practices with the creation of marine protected areas, we can make significant strides in conserving pyjama shark populations. It is essential for individuals, communities, and governing bodies to work together towards preserving these fascinating creatures and maintaining a healthy balance in our oceans.
Cultural and Economic Importance
Recreational anglers occasionally catch pyjama sharks, although their commercial value is limited. These sharks may not be the most sought-after catch, but they still contribute to the local ecosystem in important ways.
Pyjama sharks play a crucial role in regulating populations of benthic organisms. As they forage along the ocean floor, these sharks help maintain balance by controlling the numbers of prey species that dwell there. By keeping these populations in check, pyjama sharks prevent any one species from becoming too dominant or overwhelming others.
Beyond their ecological significance, pyjama sharks also hold cultural and economic importance due to their unique appearance and behavior. Their distinct striped patterns resemble those of a pair of pajamas, hence their name. This distinctive feature makes them popular among divers and snorkelers who are fascinated by the shark’s striking visual appeal.
Divers and snorkelers are drawn to observe these fascinating creatures up close in their natural habitat. Pyjama sharks provide an opportunity for underwater enthusiasts to witness firsthand the beauty and diversity of marine life. Their presence adds excitement and allure to diving expeditions, attracting tourists and contributing to local economies through recreational activities.
Debunking Myths and Fun Facts
Pyjama Sharks: No Pajamas, No Problem!
Pyjama sharks may have a name that suggests they’re ready for bedtime, but don’t be fooled! Despite their moniker, these fascinating creatures do not actually wear pajamas. It’s just a playful nickname given to them because of the striped patterns on their skin that resemble sleepwear. So, if you were expecting to find a shark in full-on bedtime attire, you might be disappointed!
Harmless Companions of the Ocean
There’s no need to worry. These gentle creatures are harmless to humans and pose no significant threat. With their small size and non-aggressive nature, encountering one while swimming or diving should be seen as an exciting opportunity rather than a cause for concern. So, next time you come across a pyjama shark during your underwater adventures, remember that they are more like friendly neighbors than fearsome predators.
A Splash of Biofluorescence
One of the most intriguing aspects of pyjama sharks is their ability to exhibit biofluorescence under certain lighting conditions. Biofluorescence is when an organism absorbs light at one wavelength and emits it at another, creating vibrant colors or glowing patterns. In the case of pyjama sharks, they can display stunning neon green fluorescence when exposed to blue light.
This phenomenon adds another layer of wonder to these already captivating creatures. Imagine exploring the depths of the ocean with UV lights illuminating the hidden beauty of pyjama sharks as they glow in brilliant hues.
Conclusion
Congratulations! You’ve now become an expert on the fascinating pyjama shark. From understanding its species to exploring its habitat, physical characteristics, behavior, and more, you’ve gained a comprehensive understanding of these remarkable creatures.
But don’t stop here! Take your newfound knowledge and share it with others. Spread awareness about the importance of conserving pyjama sharks and their habitats. Encourage others to debunk myths and learn the truth about these incredible creatures. Together, we can make a difference in protecting them for future generations to enjoy.
So go ahead, dive deeper into the world of pyjama sharks, and continue your journey of discovery. Who knows what other amazing facts and insights await you? Happy exploring!
FAQs
What is a pyjama shark?
A pyjama shark is a small species of shark found in the coastal waters of South Africa. It gets its name from the distinctive striped pattern on its body, resembling that of a pair of pajamas.
How big do pyjama sharks grow?
Pyjama sharks typically grow to be around 3 to 4 feet long, with females being slightly larger than males. They are considered to be a relatively small species of shark.
What do pyjama sharks eat?
Pyjama sharks primarily feed on small fish, crustaceans, and cephalopods. Their diet consists mainly of bottom-dwelling prey that they can find in the sandy or rocky areas where they live.
Are pyjama sharks dangerous to humans?
No, pyjama sharks are not considered to be dangerous to humans. They have small teeth and a non-aggressive nature, making them harmless unless provoked or handled improperly.
Where can I see pyjama sharks?
Pyjama sharks are native to the coastal waters off South Africa and are commonly found in shallow reefs and kelp forests. If you’re interested in seeing them up close, diving or snorkeling in these areas would provide you with the opportunity to encounter them.